You need a steady stream of several common vitamins and nutrients to keep your skin hydrated and healthy. But do you know what vitamin deficiency causes dry skin?
Lack of nutrients such as Vitamin A, Vitamin D, Vitamin C, and Vitamin E, can make the skin dry and increase the risk of skin problems such as eczema.
A typical skin condition is dry skin. Continue reading to learn how a vitamin deficiency affects the condition of your skin.
What Vitamin Deficiencies Can Cause Dry Skin?
Even though your skin is on the outside of your body, what you put inside of it matters a lot. Your skin’s support comes in large part from your diet.
A deficiency in any of the following nutrients can take a toll on the health and appearance of your skin.
1. Vitamin A

This vitamin is essential for the regeneration and repair of skin cells. Deficiency can cause accumulation of dead skin cells which can further cause problems like eczema and inflammation.
Therefore, green, yellow, and orange vegetables like carrots, spinach, sweet potatoes, oranges, mangoes, papayas, liver, beef, chicken, fish, eggs, wheat, soyabeans, etc. should be consumed in sufficient amounts to meet one’s vitamin A needs.
2. Vitamin C
Although the reputation of vitamin C is centered around its benefits for your immune system, this vitamin also has an important role in supporting hydrated skin.
Vitamin C is an essential nutrient for maintaining healthy collagen production, which is essential to the health and texture of your skin.
Because collagen plays a crucial role in the structure of your skin, it supports the elasticity and flexibility of your skin. Collagen also helps support hydrated skin — and if you are lacking in vitamin C, you may experience dry skin.
You can consume more vitamin C by eating peppers, citrus fruits, and leafy greens, among other foods. Supplements containing vitamin C are also widely used and simple to incorporate into your daily routine.
3. Vitamin D
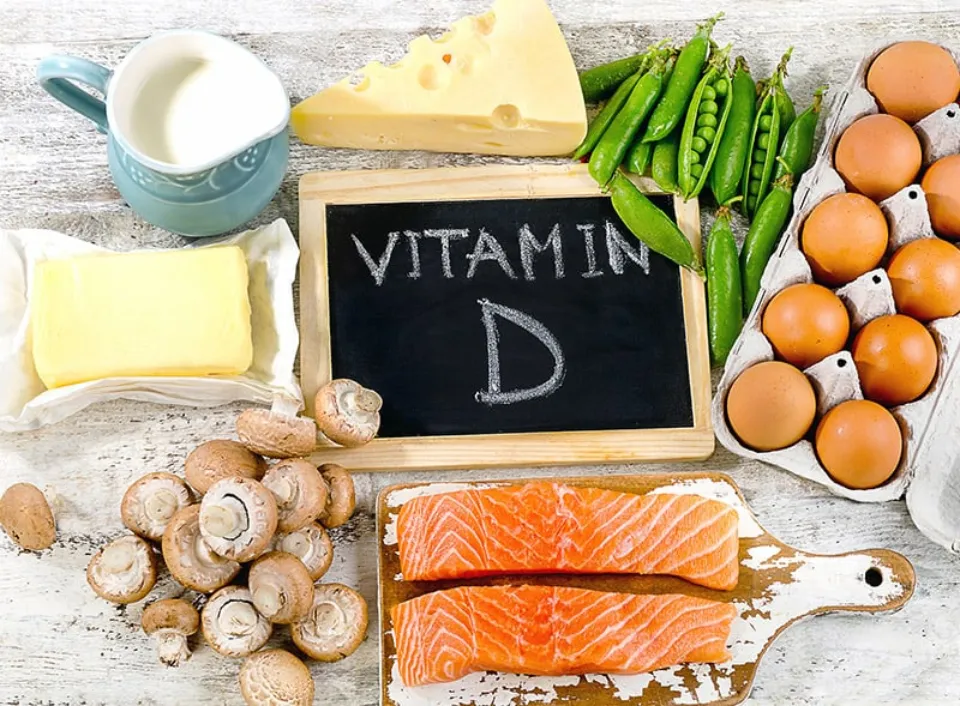

Despite being derived from sunlight and known as the “sunshine vitamin,” vitamin D hydrates your skin, which the sun’s rays cannot.
Vitamin D contributes to the skin’s natural barrier, which traps moisture as a result, helping your skin retain moisture.
Additionally, this vital vitamin can aid in calming skin dryness and irritability. Vitamin D relieves the skin, which helps keep the skin’s natural moisture.
Sunlight can cause the skin to produce vitamin D, but it can also be obtained from a number of foods. Salmon, red meat, egg yolks, and fortified goods like cereals and milks are some examples of foods high in vitamin D.
4. Vitamin E
This vitamin is crucial for maintaining the moisture and hydration of the skin. Lipids’ oil base, vitamin E, helps to fight off inflammation and the early signs of aging.
Lack of vitamin E can cause dryness and cracks on the skin. For the purpose of repairing skin cracks and shielding it from additional harm, vitamin E is also crucial.
Sunflower seeds, almonds, peanuts, pumpkin, pepper, safflower and soybean oils, among other foods, are good sources of vitamin E.
Related Reading: How to Use Vitamin E Oil on Face?
5. Collagen
Just like vitamin C deficiency, but more direct, lower amounts of collagen in the body can result in or exacerbate dry skin. Although the body produces collagen naturally, this process slows down as we get older.
If you don’t get enough vitamin C, smoke, eat too much sugar, or spend too much time in the sun, your body may start to produce less collagen. All of these can degrade the body’s collagen, which increases the likelihood of wrinkles, reduces skin elasticity, and causes dry skin.
In most health food stores, you can typically find collagen supplements, which are typically made from animal products.
Given that the body naturally produces collagen, taking vitamin C and additional nutrients like zinc and copper can support collagen synthesis.
Read More: Does Drinking Water Help Dry Skin?
6. Lutein and Zeaxanthin
Both the little-known and highly advantageous compounds lutein and zeaxanthin. These two substances are potent carotenoids—classes of pigments that are present in plants.
Due to their high antioxidant content, these pigments can support overall eye and skin health. Both carotenoids function as potent UV filters in your skin and eyes, protecting both organs from damage when exposed to UV rays.
The carotenoids can thus assist in preserving the health, youthfulness, and texture of your skin.
These pigments can protect your skin from free radical damage because they are high in antioxidants. Free radicals damage your cells and can cause early aging and damage to the skin cells. You can support the health of your skin by regularly ingesting these antioxidant-rich carotenoids.
These two carotenoids help to support your skin’s hydration as well as its longevity, making them beneficial for skin health. To keep your skin hydrated and healthy for a longer period of time, carotenoids can help shield it from water loss.
As it gives the tiny ocean creatures their pinkish-red color, krill is a typical source of zeaxanthin. For those who avoid consuming animal products, lutein is also present in some plant-based supplements and in marigold flowers.
7. Probiotics
An organ that is alive and bursting with life is your skin. The skin’s microbiome, which is home to billions of beneficial bacteria, is unique. By keeping irritants and stressors out, the bacteria on your skin help you stay properly hydrated.
Probiotics are important for supporting the quantity and variety of bacteria in the body, which supports the durability of the skin barrier and can aid in reducing unneeded water loss.
Probiotics support the health of your gut microbiome, which strengthens your immune system as well. Your body can absorb nutrients better with a stronger gut microbiome, which can help you avoid potential nutrient deficiencies in addition to that.
Yogurt and foods that have been fermented, such as kimchi, sauerkraut, and even pickles, are sources of probiotics. Probiotic supplements come in a huge range and can be found in both pill and food form.
8. Zinc
Like vitamin C, zinc is better known for its ability to support the immune system and less for its ability to soothe dry skin.
But zinc is yet another crucial element in preventing dry skin. In actuality, zinc’s capacity to support a strong immune system also plays a significant part in supporting hydrated skin.
One of the biggest threats to hydrated skin is irritation. Zinc supports your immune system and your body’s natural defenses, which helps you maintain supple, healthy, and hydrated skin. In order to prevent the potential effects of irritated skin, zinc aids in maintaining these defenses.
Again similar to vitamin C, zinc has an important role in supporting healthy collagen production.
This mineral therefore aids in preserving the hydration and toughness of your skin. Seafood, meat, beans, nuts, seeds, and soy products are common sources of zinc.
Takeaway: What Vitamin Deficiency Causes Dry Skin
Dry skin may not always be due to changes in weather or use of harsh, chemical-laden products.
Consult a doctor to learn the precise cause of your dry, itchy skin if it appears suddenly or if it has been a long time since it did.
FAQs
How to Treat Dry Skin Internally?
Water consumption increases skin hydration, keeping it supple.
Does B12 Deficiency Cause Dry Skin?
Your skin can suffer from a vitamin B deficiency, which can result in acne, rashes, dry, flaky skin, cracked lips, and wrinkles.
Why is My Skin So Dry Even When I Moisturize?
It may simply be the case that you’re applying the wrong moisturizer to your skin or that you’re applying too much of it.