Many people have questions about hair loss, with the most frequent one being “Is hair loss genetic?”
Yes, hair loss can be hereditary. Although the degree to which genetics affect hair loss can vary, it is believed that up to 80% of cases of androgenetic alopecia are caused by genetic factors.
In this article, we’ll look at the genetics of balding and discuss ways to prevent hereditary hair loss.
Is Hair Loss Genetic?
Genetics play a large role in determining how much hair loss you’ll see as you age. However, other elements—such as stress levels, diet, and medications—also contribute to baldness.
Although genetic hair loss cannot be stopped, there are steps you can take to minimize it and maximize your hair growth potential.
You Might Also Like: Can Hair Loss Be Reversed?
What Causes Hereditary Hair Loss?
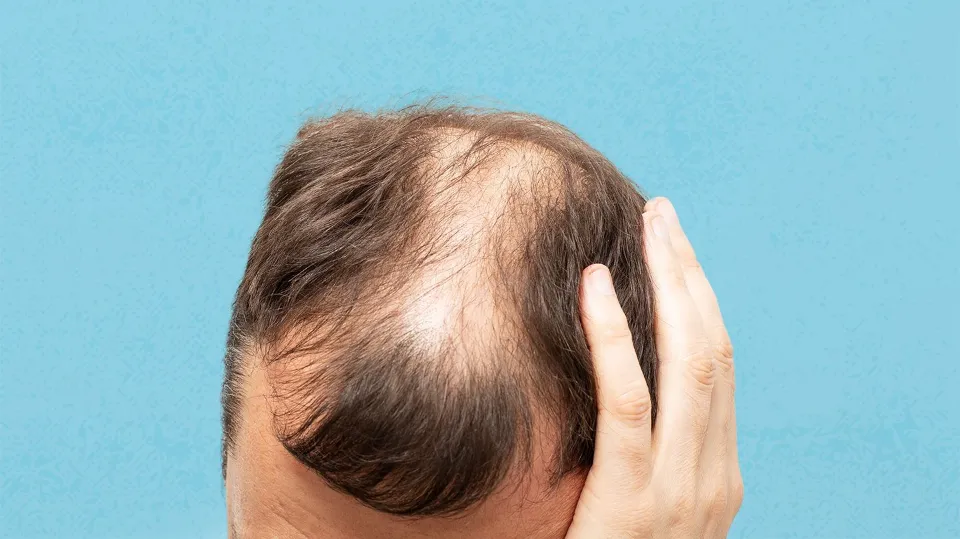
The progress of hereditary hair loss is dependent on the hair cycle itself and the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
One of the main causes of hair loss is DHT, a testosterone-related male sex hormone. It is highly likely that you are sensitive to DHT if you are genetically predisposed to hair loss.
The hair growth cycle is shortened by DHT, which means that less time is spent in the growth stage before the hair eventually falls out. The hair that grows in to replace the lost strand is typically finer and shorter, and eventually the follicle will shut down and the hair will stop growing.
Consequently, the hair will gradually become thinner and eventually fall out. Miniaturization is the name of this process.
Related Reading:
- Does Alcohol Cause Hair Loss?
- Can Hair Dye Cause Hair Loss?
- Can Dry Scalp Cause Hair Loss?
- Does Creatine Cause Hair Loss?
- Does Dandruff Cause Hair Loss?
- Does Hard Water Cause Hair Loss?
- Does Dry Shampoo Cause Hair Loss?
Is There Anything I Can Do to Beat Hereditary Hair Loss?
Hair loss caused by genetic factors is permanent and there’s little you can do to stop it.
However, there are a number of ways to slow it down.
- healthy lifestyle choices. Your overall health and the health of your hair can be supported by eating a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, reducing stress, and exercising frequently.
- Topical medications. The first line of treatment is frequently topical drugs like minoxidil (Rogaine). In balding areas, you typically apply these creams directly to your scalp.
- Oral medications. For the treatment of MPB, your doctor might suggest taking oral medications like finasteride (Propecia). Also, an enlarged prostate can be treated with finasteride.
- surgery to transplant hair. Follicular unit transplantation and follicular unit extraction are two types of hair transplantation procedures that transfer hair follicles from one area of your scalp to balding areas.
- (Red light therapy) Laser therapy. Laser therapy may help improve hair densityTrusted Source if you’re dealing with genetic hair loss or hair loss from chemotherapy. To ascertain the efficacy of this treatment option, more research is required.
- Injections of platelet-rich plasma. Injections of platelet-rich plasma may aid in promoting hair growth where it is being lost. Similar to laser therapy, further study is required to determine its efficacy.
What Else Causes Balding?
Along with genetics, a variety of other factors can contribute to hair loss in people of any gender.
Due to hormonal changes, hair loss is frequently noticed by women after menopause, whereas balding is typically first noticed by men in their early 20s.
- Hormonal changes. Hormone changes are a common cause of hair loss in women following menopause, childbirth, and pregnancy. Changes in thyroid hormone levels can cause hair loss in both men and women.
- Alopecia areata. Patchy hair loss is a symptom of alopecia areata, an immune disorder.
- Trichotillomania. Trichotillomania is a mental illness that makes you want to pull out your own hair. It is also known as hair-pulling disorder.
- additional health problems. Hair loss is a symptom of a number of medical conditions, including ringworm infections, cicatricial alopecia, and traumatic alopecia.
- Certain hairstyles. Tight ponytails and other hairstyles that strain your hair can cause traction alopecia, a type of hair loss. Permanent or temporary hair loss can occur in this situation.
- supplements and medications. Drugs used to treat the following medical conditions may lead to hair loss:
- depression
- heart problems
- gout
- high blood pressure
- cancer
- arthritis
- Birth control. The use of birth control pills is stopped suddenly may cause temporary hair loss as well.
- Radiation therapy. Hair loss is a frequent side effect of radiation therapy, which is frequently used to treat cancer. This hair loss is frequently only temporary.
- Stress. Temporary hair thinning can be caused by prolonged physical or mental stress.
- lack of nutrition. Your hair growth may suffer if you do not consume enough protein or other crucial nutrients, such as zinc.
Conclusion: is Hair Loss Genetic
Genetics can influence hair loss, no matter your gender. Though the exact genes involved in balding’s genetic component are still not fully understood, many different genes are likely to play a role.
Even though genetic hair loss is irreversible, certain medications, laser treatments, and platelet-rich plasma injections may encourage hair growth in balding areas. To cover bald spots, some people also get hair transplants.
FAQs
Is Baldness Hereditary from Mother Or Father?
The hereditary factor is more dominant on the mother’s side.
How to Tell If Hair Loss is Genetic Or Stress?
You may experience stress-related hair loss if your daily hair loss exceeds the typical 80–100 strands.
What Does Hair Loss from Stress Look Like?
Telogen effluvium, also known as stress hair loss, resembles sudden hair loss after brushing, washing, or even just touching the hair.




