Thirty percent of the protein in your body is collagen. What is collagen exactly?
Collagen is a molecule. It is a tough, insoluble, fibrous protein.
It is a key component of the extracellular matrix, a network of molecules that holds together the body’s tissues.
Everything you need to know about collagen is provided in the following paragraphs.
What is Collagen?
Collagen is the most abundant protein in your body. It makes up about 30% of its total protein.
The main component of your body’s skin, muscles, bones, tendons, ligaments, and other connective tissues is collagen. Additionally, it can be discovered in your blood vessels, intestinal lining, and organs.
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Proline, glycine, and hydroxyproline are the three main amino acids used to make collagen.
These amino acids band together to create protein fibrils with a triple helix structure. The right quantities of vitamin C, zinc, copper, and manganese are also required by your body to create the triple helix.
What is Collagen Made Of?

The main amino acids that make collagen are proline, glycine and hydroxyproline.
The triple helix structure of protein fibrils is created by the association of these amino acids.
The right quantities of vitamin C, zinc, copper, and manganese are also required by your body to create the triple helix.
What Does Collagen Do?
Collagen’s main role is to provide structure, strength and support throughout your body.
Collagen’s specific roles include:
- Fostering fibroblast formation in your dermis, the middle layer of your skin, which promotes the development of new cells.
- Replacement of skin cells lost to aging.
- Giving organs a shield of protection.
- Supplying your skin with a structure, strength, and elasticity.
- Facilitating blood clotting.
Read More: Does Collagen Help With Hair Loss?
Are There Different Types of Collagen?
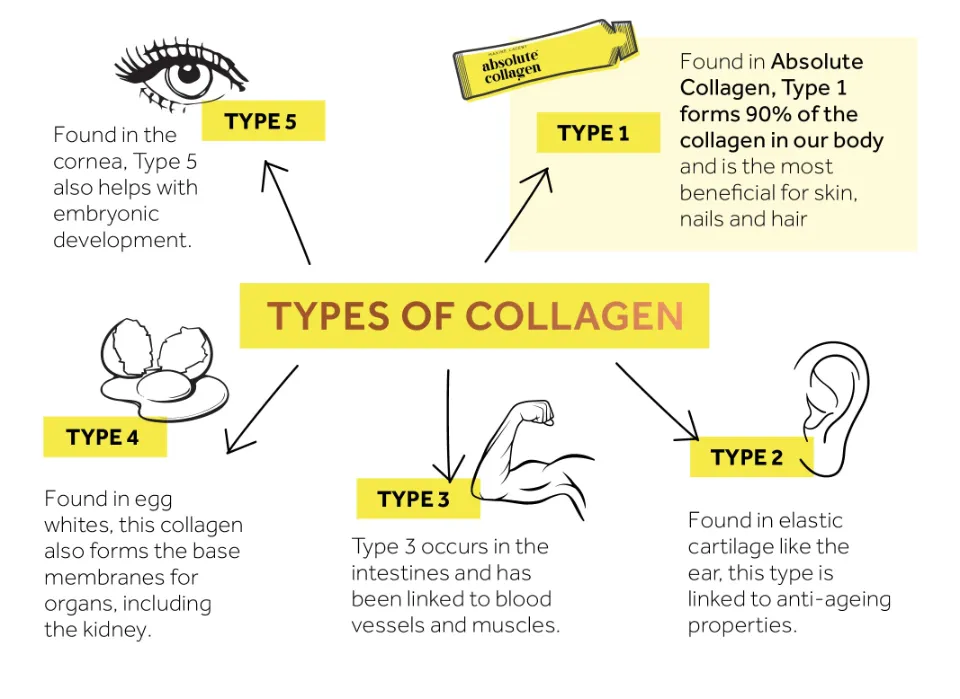
Some 28 types of collagen types have been identified.
They differ in the way the molecules are put together, the cell components that are added, and the locations in which the body uses the collagen. There is at least one triple helix structure present in every collagen fibril.
The main five types of collagen and what they do are:
- Type I. In your body, 90% of the collagen is of this type. Your skin, bones, tendons, and ligaments are structurally supported by type I, which is tightly packed.
- Type II. Elastic cartilage, which supports joints, contains this type.
- Type III. Organs, arteries, and muscles all contain this type.
- Type IV. The layers of your skin contain this kind.
- Type V. The cornea of your eyes, some skin layers, hair, and placental tissue all contain this type.
What Causes Collagen Loss?
As you age, your collagen production naturally declines. The distribution and fragmentation of collagen also change.
These modifications result in wrinkles and dry, sagging skin, which are typical signs of aging. Age-related declines in bone strength are also accompanied by a decrease in the integrity of the collagen found in the skeletal system.
While collagen deterioration and loss as you age are unavoidable, some dietary and lifestyle choices can hasten this process.
For instance, it is well known that smoking cigarettes degrades collagen, which results in skin aging, wrinkles, and loss of elasticity.
In addition to lowering collagen production and harming skin repair mechanisms, excessive drinking has been shown to hasten skin aging.
In addition, eating a diet high in processed foods and added sugars can speed up the aging process by promoting the glycation process, which slows down collagen turnover and interferes with collagen’s ability to interact with other proteins and cells in the body.
Excessive sun exposure degrades collagen production as well, so wearing sunscreen and avoiding excessive sun exposure can help prevent signs of premature skin aging
Conclusion: What is Collagen
Collagen is a protein that the body produces. It is fundamental to the development and maintenance of connective tissue, cartilage, and the skin.
Dressings that facilitate wound healing include collagen in medicine.
To improve their skin, many people use products that either contain collagen or help the body produce more of it. Some of these may work. However, more investigation is required.
FAQs
What is Collagen Good For?
Your skin, muscles, bones, and connective tissues are given structure, strength, or support by it.
What Foods Are High in Collagen?
- Beef Bone Broth.
- Skin-On Chicken.
- Pork Bone Broth.
- Sardines.
- Organ Meats.
- Drinks infused with collagen.
- Gummy Candy.
- Berries.
Which Fruit is Rich in Collagen?
Citrus fruits like orange, lemons, limes, and grapefruit are known for being foods high in collagen-producing properties.




